Geothermal heating and cooling is a sustainable and efficient technology that uses the Earth’s stable underground temperatures to manage indoor climates. Unlike traditional HVAC systems that depend on fossil fuels or electrical resistance, geothermal systems harness renewable energy from the ground to provide heating, cooling, and even hot water. This method greatly reduces energy consumption and environmental impact while ensuring comfort throughout the year.
How Does Geothermal Heating and Cooling Work?
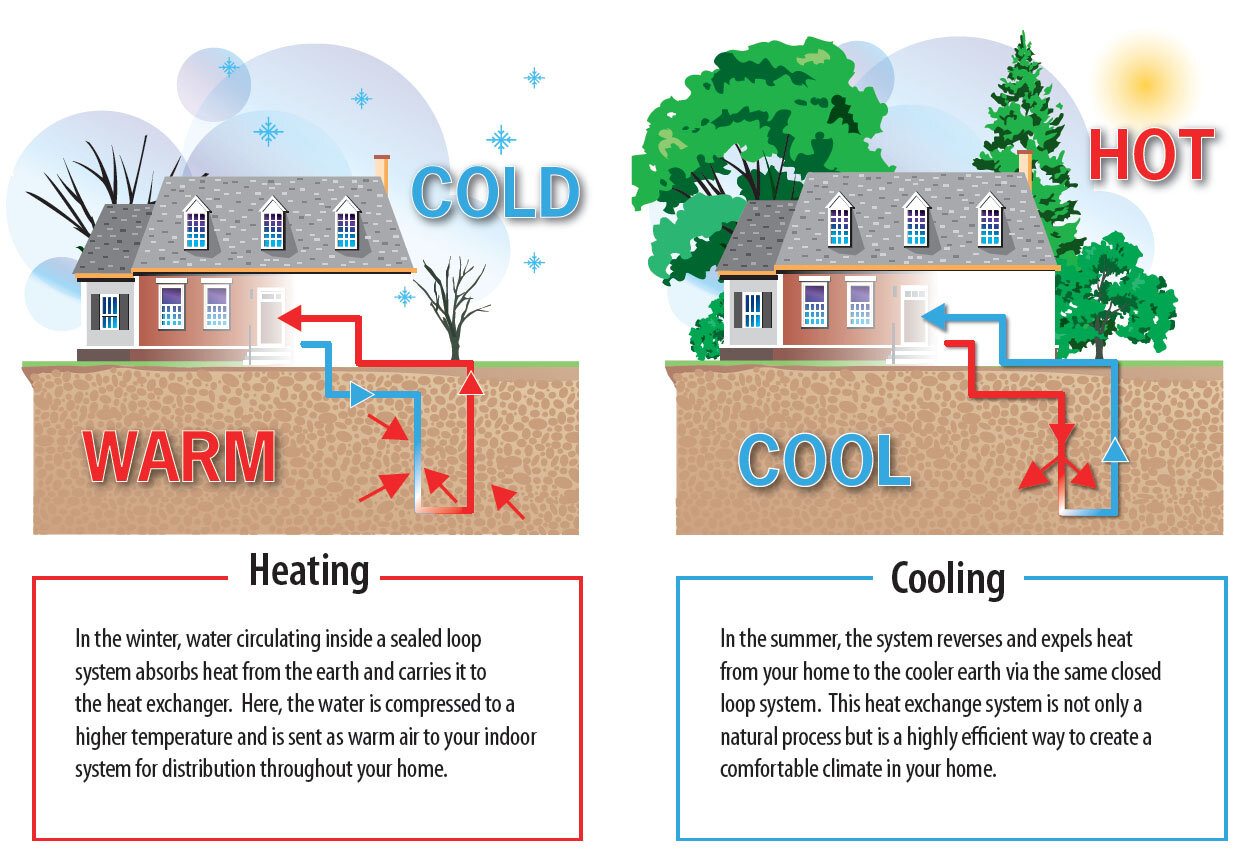
Geothermal heating and cooling systems function by transferring heat to and from the ground through a network of pipes, known as a ground loop, and a heat pump. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. The Ground Loop System
The ground loop is installed below the Earth’s surface and can be configured horizontally, vertically, or in a pond/lake, depending on the available land and geological conditions. This loop circulates a heat-transfer fluid (either water or a water-antifreeze mixture) to exchange thermal energy with the ground.
Heating Mode: During colder months, the fluid absorbs heat from the ground, which remains relatively warm even in winter.
Cooling Mode: In warmer months, the system reverses, transferring heat from the building into the cooler ground.
2. The Heat Pump
The heat pump is the heart of the system, responsible for extracting or dispersing heat. It operates similarly to a refrigerator but in reverse:
- In heating mode, the heat pumps extracts heat from the fluid and amplifies it using a compressor before distributing it throughout the building.
- In cooling mode, the process is reversed, removing heat from the indoor air and transferring it to the ground loop.
3. Distribution System
- The conditioned air is circulated within the building using standard ductwork or radiant floor systems, ensuring consistent and even temperature control.
3. Lower Operating Costs
While the upfront cost of installing geothermal systems may be higher, the long-term savings on energy bills and the low maintenance needs make them a cost-effective choice over time.
4. Durability and Longevity
The underground loops can endure for 50 years or more, and the heat pumps typically last around 20 years, providing a dependable and lasting solution.
5. Quiet and Comfortable
Geothermal systems run quietly and maintain steady indoor temperatures, avoiding the noise and temperature swings that often come with traditional systems.
Types of Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems
Depending on the layout of the property and its specific requirements, various configurations can be utilized:
1. Horizontal Ground Loops
Best suited for properties with plenty of land, this setup involves laying pipes in shallow trenches. It is cost-effective but needs more space.
2. Vertical Ground Loops
This option works well for properties with limited space. Pipes are placed in deep boreholes, making it pricier but more efficient in terms of land use.
3. Pond/Lake Loops
If there is a nearby water body, loops can be submerged to exchange heat with the water, which can lower installation costs.
4. Open-Loop Systems
These systems utilize groundwater as the medium for heat transfer, which is then returned to the source. They are efficient but depend on a reliable and sustainable water supply.
Applications of Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Geothermal systems are adaptable and can be employed in:
- Residential Buildings: Offering efficient heating, cooling, and hot water solutions.
- Commercial Spaces: Lowering energy expenses in offices, schools, and hospitals.
- Industrial Facilities: Ensuring stable indoor climates for manufacturing and storage.
The installation process for geothermal heating and cooling systems consists of several key steps:
- Site Evaluation: This involves assessing the availability of land, analyzing soil composition, and considering local climate conditions.
- System Design: Here, the ground loop and heat pump configuration are tailored to meet specific needs.
- Excavation and Loop Installation: This step includes drilling or trenching to set up the ground loop.
- Heat Pump Connection: The next phase is connecting the loop to the heat pump and the distribution system.
- Testing and Commissioning: Finally, this ensures that the system operates at optimal performance and efficiency.
Is Geothermal Heating and Cooling Right for You?
Although geothermal systems provide numerous advantages, they may not be the best fit for everyone. Important factors to consider include:
Initial Cost: The upfront investment can be significant, but tax incentives and rebates may help reduce the overall expense.
Land Requirements: Adequate space is necessary for either horizontal loops or boreholes.
Climate: These systems work best in areas with moderate heating and cooling needs.
The Future of Geothermal Heating and Cooling
As the global community moves towards sustainable energy solutions, geothermal heating and cooling is set to play a vital role in decreasing dependence on fossil fuels. Innovations like enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and hybrid systems are making this technology more efficient and accessible, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Geothermal heating and cooling represents a transformative solution for environmentally conscious homeowners and businesses. By utilizing the Earth’s natural energy, it provides outstanding comfort, efficiency, and sustainability. While the initial cost may appear intimidating, the long-term savings and environmental advantages make it a valuable investment. Whether you are constructing a new home or upgrading an existing HVAC system, geothermal technology is a wise and progressive choice.